The top part of a mushroom. Generally flat, convex, campanulate or conical in shape. Primary function of the cap is to protect the spore-producing surface underneath.
The period during the life cycle of fungi, before the fruiting stage, where mycelium grows throughout the substrate or other mediums such as grain or agar.

Any undesired foreign organism living on a growing medium (substrate, spawn, fruiting blocks, agar plates). Contamination is typically bacteria and often occurs due to improper sterile technique.

The act of growing fungi, either indoors or outdoors.

The content of water remaining in a soil after being saturated with water and after free drainage is negligible. Generally described as the state achieved after squeezing a handful of substrate with only a couple drops of water dripping out.

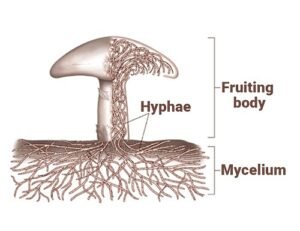
The development of fruiting bodies in a quick succession. A “crop” of mushrooms. After harvesting a flush there is a resting period before the next flush.

A process of the reproductive stage where mycelium begins to produce mushrooms for the purpose of spore propagation.

The conversion of spores from a dormant biological organism to one that grows vegetatively.
Tiny structures layered side-by-side on the underside of a mushroom cap, with the primary function of producing and releasing billions of spores; also called hymenium.

An air-tight apparatus which has two holes in the side where gloves are permanently attached to the rims of the holes. In mycology, it is used to keep contaminants out or keep fumes or infectious agents from escaping.

Microscopic long filamentous branches found in fungi, the developmental unit of mycelium.
An enclosed workspace that uses HEPA filters and forced air to create a sterile workspace.

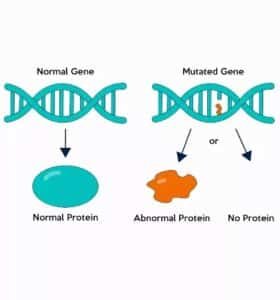
Permanent change in a gene.
The vegetative part of fungi which consists of vast, complex networks of cells that form thin white fibers.

The study of fungi.

A species of very potent hallucinogenic mushrooms.

Heat treating substrate to kill unwanted organisms while still keeping favorable organisms alive. The temperature range is 60°C to 80°C(140°F-175°F).

A glass container consisting of a circular, flat dish with vertical sides, and a similar but slightly larger cover which fits over it. Standard equipment for the growth of microorganisms in pure culture.

Beginning of the mushroom fruiting stage, tiny fruiting bodies with caps the size of a pin.

The stage before pinheads, the initial fruiting body.

Another active compound found in magic mushrooms alongside its counterpart psilocybin.
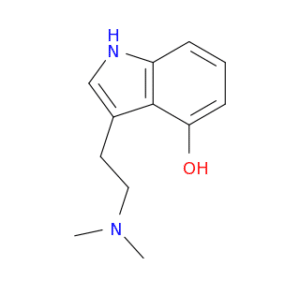
A hallucinogenic compound that can be found in many species of psychedelic fungi such as Psilocybe cubensis.
A person who explores altered states of consciousness through the use of psychedelic drugs.

A ratio expressed as a percentage of the amount of moisture present relative to the amount that would be present if the air were saturated.

Type of mycelium growth. Appears as a root-like mycelial strand composed of bunched parallel hyphae. Associated with strong and plentiful fruits.

The stipe of stalk of a mushroom with the primary function of elevating the cap to assist with wide dispersal of spores.

Dense mycelium growth that ceases fruiting. It could be triggered by environmental factors or from being exposed to petroleum-based fumes/chemicals.

Type of mycelium growth. Cotton-ball-like appearance mycelium.

A common green pathogenic fungus (mold) that gains entry primarily through contaminated equipment and personnel.

The raised area in the center of a mushroom cap. Resembles a nipple.

A thin membrane that attaches the edge of a mushroom cap to the stem. The veil tears away from the cap once the mushroom reaches maturity, often leaving a partial veil hanging on the stem.
